Transarterial Chemoembolization
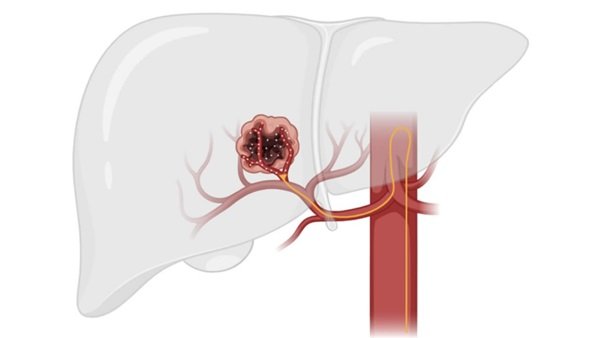
🔹 What is TACE?
- Minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer.
- Chemotherapy delivered directly to tumor artery.
- Blood supply to tumor blocked → tumor starved of oxygen & nutrients.
- Healthy liver tissue mostly spared.
🔹 Who Benefits?
- Intermediate-stage HCC (confined to liver).
- Patients not eligible for surgery or transplant.
- Bridge therapy before liver transplant.
- In selected cases: combined with other therapy like ablation.
- ❌ Not suitable for poor liver function or widespread cancer.
🔹 Procedure
- Catheter inserted via groin or wrist artery.
- Guided into hepatic artery (under Fluoroscopy).
- Chemo + embolic beads injected.
- Blood flow to tumor blocked.
⏱ Time: 1–2 hrs | 🏥 Hospital stay: 2–5 days
🔹 Recovery
- Common: mild fever, nausea, pain, fatigue (few days).
- Resume normal activity in ~ 1 week.
- CT/MRI follow-up at 4–6 weeks.
- Multiple sessions may be needed.
🔹 Benefits
✅ Minimally invasive, repeatable.
✅ Tumor-targeted therapy, less side effects.
✅ Improves survival in intermediate HCC.
✅ Can serve as bridge to transplant.
🔹 Risks
- Short-term: fever, nausea, pain.
- Temporary liver function decline.
- Rare: infection, non-target embolization.
🔹 FAQs
- Curative? → No, but effective for control & survival.
- Sessions? → Varies by patient and tumor size.
- Success rate? → ~60–70% tumor control.
- Recovery time? → 5–7 days.
- Lifestyle? → Liver-friendly diet, no alcohol, regular follow up scans.
- Combinations? → Possible with ablation, other systemic therapy, or before transplant.
